Burns are injuries to the skin or deeper tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. Because burns can damage the skin and other body parts, they need special attention. Nursing care for patients with burns is vital for healing, comfort, and preventing problems. With the right care, patients can recover faster and avoid serious risks. This guide explains the best practices for burn wound care, burn injury recovery, and burn prevention tips.
Common Types and Causes of Burns
Burns can happen in many ways. Understanding the types and causes helps in giving the right care. For example, burns are grouped by what caused them:Thermal burns: Caused by hot objects, flames, steam, or hot liquids.Chemical burns: Result from contact with strong acids or cleaning products.Electrical burns: Happen when electricity passes through the body.Radiation burns: Caused by sun exposure or medical treatments like radiation therapy.
Common causes include kitchen accidents, house fires, faulty wiring, and sunburn. In some areas, open flames or unsafe cooking methods increase the risk.
Immediate First Aid for Burn Injuries
Quick action can make a big difference after a burn. If you or someone else is burned, follow these steps:Remove the person from the source of the burn.Cool the burn with cool (not cold) running water for at least 10 minutes.Remove tight clothing or jewelry near the burn, but do not pull off anything stuck to the skin.Cover the burn with a clean, non-stick cloth or bandage.Do not apply ice, butter, or creams to the burn.Keep the person warm and calm.Seek medical help for large, deep, or facial burns.
These steps help reduce damage and lower the risk of infection.
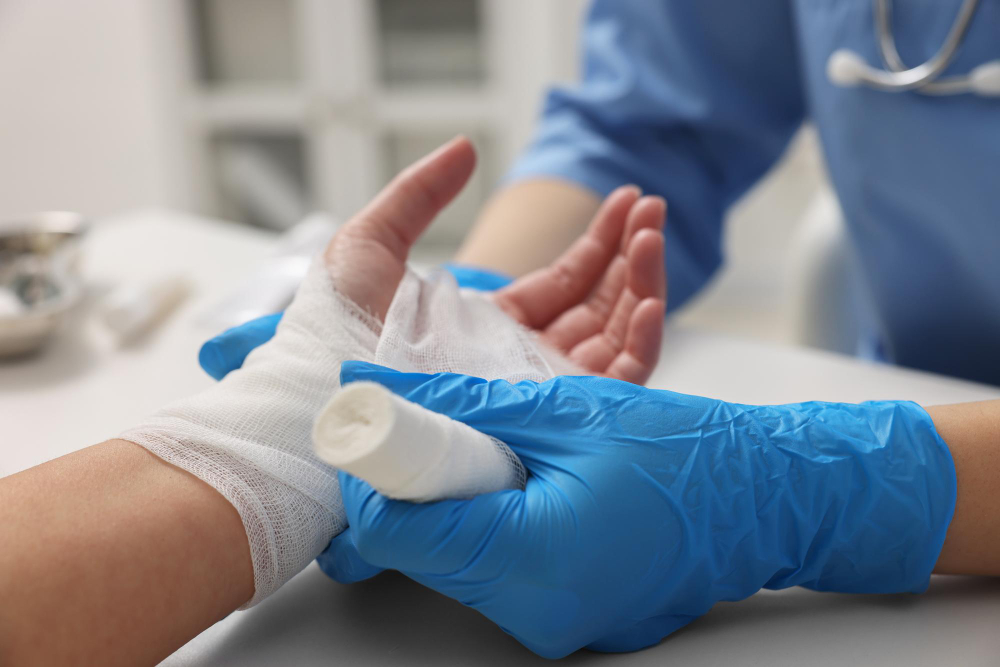
Key Principles of Nursing Care for Burn Patients
Nurses play a key role in burn wound care and burn injury recovery. Their main goals are to protect the wound, ease pain, and support healing. Here are the most important principles:Wound assessment: Nurses check the size, depth, and location of burns. This helps plan the right care.Infection prevention: Burns can get infected easily. Nurses use clean tools, wash hands, and change dressings often.Pain management: Pain is common with burns. Nurses give pain medicine and use gentle care to keep patients comfortable.Hydration: Burns can cause fluid loss. Nurses watch for signs of dehydration and give fluids as needed.Monitoring vital signs: Nurses check heart rate, breathing, and temperature often. This helps spot problems early.
Following these steps helps patients heal safely and quickly.
Ongoing Care and Recovery Support
After the first treatment, ongoing care is important for full recovery. Nurses and caregivers focus on these areas:Wound dressing: Dressings protect the burn and help it heal. Nurses change them often and watch for signs of infection.Mobility support: Gentle movement and exercise prevent stiffness and help the body recover.Nutrition: Eating healthy foods gives the body energy to heal. Nurses may suggest high-protein meals and plenty of fluids.Emotional support: Burns can be scary and painful. Nurses listen, offer comfort, and help patients cope with stress.Patient education: Nurses teach patients and families how to care for wounds, spot problems, and prevent future burns.
With the right support, patients can regain strength and confidence.
Prevention Tips for Burn Injuries
Many burns can be prevented with simple steps. Here are some burn prevention tips for home and the community:Keep hot liquids and sharp objects out of children’s reach.Install smoke alarms and check them often.Set water heaters to a safe temperature (below 120°F or 49°C).Use oven mitts and pot holders when cooking.Store chemicals and cleaning products safely.Wear sunscreen and protective clothing outdoors.Teach children about fire safety and emergency plans.
By following these tips, you can lower the risk of burns for yourself and your loved ones.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Some burns need professional care right away. Seek medical help if you notice:Burns larger than your palmBurns on the face, hands, feet, or groinDeep burns with white, charred, or leathery skinSigns of infection (redness, swelling, pus, fever)Trouble breathing or burns from electricity or chemicals
Quick action can prevent serious problems and help healing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What should I do if a burn blisters?
Do not pop the blister. Cover it with a clean bandage and keep it dry. If it breaks, clean gently and watch for infection.
How often should burn dressings be changed?
Dressings should be changed as advised by your nurse or doctor, usually once a day or when wet or dirty.
Can I use home remedies like toothpaste or butter on burns?
No, do not use home remedies. They can make burns worse or cause infection. Use cool water and seek medical advice.
How long does burn injury recovery take?
Recovery time depends on the burn’s size and depth. Small burns may heal in days, while larger burns can take weeks or months.
Is emotional support important for burn patients?
Yes, emotional support helps patients cope with pain, stress, and changes in appearance. Nurses and families play a big role in recovery.
Contact us today to book nursing care services at home.